The purpose of quality management process is to ensure that the project conforms to the mutually agreed requirements, specifications, and expectations. The aim is to measure the progress of the project while assessing its performance to determine whether it satisfies the function intended for the project. This process is founded on the PMBOK framework thereby confirming that it is a proven practice that is applied widely in project management.
The quality management is carried out to ensure that the final product of the project complies with the quality standards and regulations that have been put in place. It should therefore be carried out throughout the project, from the initiation of the project to its closure. This should be done both internally, that is, for the company, project team, PMO, and the project manager, and externally, for the clients and the stakeholders.
Thus, the process helps to monitor the final results of a project on both the management level and the product to determine if they correspond to the set standards and establish what could be done to improve the results to meets the standards.
This process is critical as it helps in ensuring that the deliverables acquired can meet the requirements of the customer, this therefore improves the quality of the deliverables.
The objectives of the quality management process are:
- To set the quality targets to be met by the project team
- To define how the set quality targets are to be measured
- To take all necessary actions to measure the project quality
- To report on the overall level of quality achieved on the project
The scope of the quality management process involves both the internal and external stakeholders of the project, to ensure that all set standards for the project are met to ensure optimal quality of the project’s results.
Thus, the scope of the process involves:
- Developing a quality management plan
- Testing and inspecting planning
- Undertaking process and documentation audit
- Performing quality assurance
- Undertaking product testing and quality control
- Implementation of change
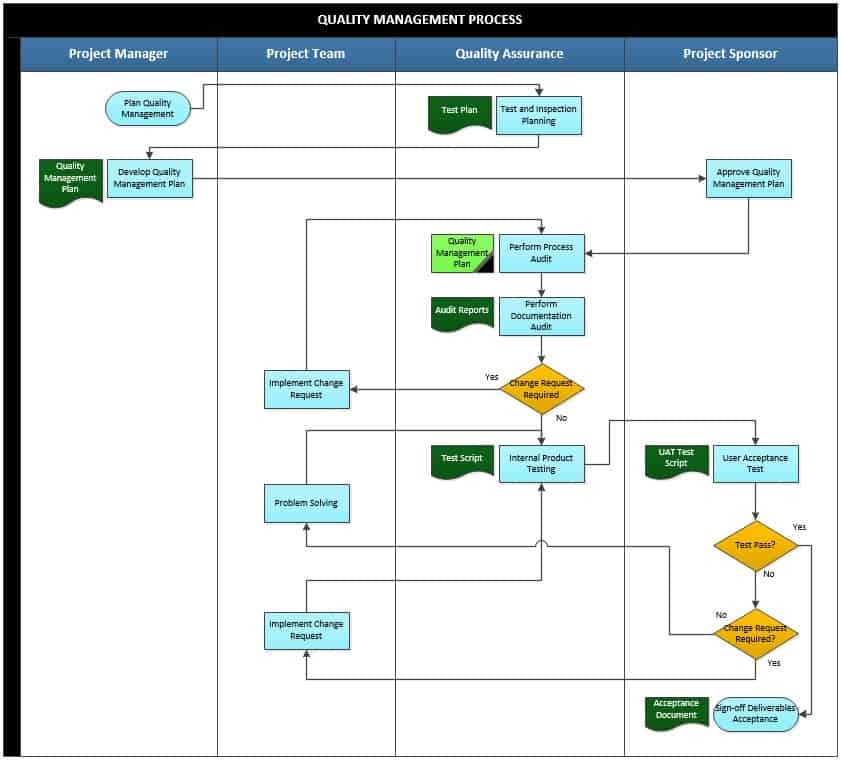
1. Plan Quality Management
Planning quality management involves defining the quality management process to achieve the results needed. The process needs to be defined and detailed with all the expected results identified.
The project manager is tasked with the planning of the quality management process. This planning process touches on all the aspects of the scope of the project as they all determine the quality of the final results of the project.
2. Test and Inspection Planning
This activity aims at planning on how tests and inspections will be carried out for quality assurance. The quality assurance team plans on what should be considered and how the test and inspection will be carried out to measure the quality targets set out for the project. This is done to ensure that the final results and product of the project complies with the standards and regulations put in place.
The Test Plan is the output document for the test and inspection planning activity. It details how the tests and inspection will be conducted on the project to measure its level of quality.
3. Develop Quality Management Plan
The purpose of this activity is to establish a plan on how to manage the quality of the results and deliverables to be achieved from the project. This puts in place a well-elaborated plan on the prediction and prevention of quality problems, and the inspection of the final results of the project to determine their compliance with the set standards. The project manager develops the quality management plan while putting into consideration all the quality standards that were set for the project.
To develop the quality management plan, it will require all the documents detailing the quality standards and regulations to be used. These documents may include the company’s quality policy, standard descriptions, and the project scope statement.
The Quality Management Plan is the output document for this activity. The quality management plan is passed over to the project sponsor for approval. The project sponsor goes through the whole document to make sure that it covers all the aspects required for the quality management of the project. The project sponsor then approves the quality management plan.
4. Perform Process Audit
The aim of this activity is to carry out an audit on the project management processes. The quality assurance team carries out the audit to ensure that the project’s quality management process is in line with the requirements, specifications and expectations of the clients. This audit is carried out following the quality management plan developed for the project. This ensures that all set standards are met, and the regulations duly followed.
The Quality Management Plan document is used as the point of reference during the process audit. This ensures that the auditing process covers all necessary aspects required in ensuring the quality of the final product.
Related Articles:
- Project Initiation Process: 6 Key Activities
- Project Planning Process: 7 Key Activities
- Project Execution Process: 8 Key Activities
- Project Monitoring and Control Process: 10 Key Activities
- Project Closing Process: 8 Key Activities
- Project Handover Process: 11 Key Activities
- Risk Management Process: 11 Key Activities
- Change Control Process: 8 Key Activities
- Issue Management Process: 9 Key Activities
5. Perform Documentation Audit
The objective of this activity is to carry out an audit on all the documentations made on the project. The quality assurance team performs the audit to make sure that the information contained in those documents is in line with the practices and procedures carried out in the project. This ensures that all activities and timelines carried out in the project are in line with the initial projections.
It also ensures that each person involved in the project satisfactorily carries out their roles to ensure that the project achieves its expectations without compromising the quality of the deliverables. The output document for the perform documentation audit activity is the Audit Reports. These reports detail the findings of the audit performed by the quality assurance team on the project’s documentation.
6. Change Request
From the findings of the audits performed, the quality assurance team is tasked with determining if there is any change request required. If there is, it is forwarded to the project team for implementation. After the implementation of the change request, the process moves back the Perform Process Audit activity by the quality assurance team. If there is no change request, the process moves to the next activity.
7. Internal Product Testing
This activity aims to internally run tests on the products of the project. The quality assurance team runs the test on the products to ensure that it meets all the requirements, specifications and expectations intended at the very beginning. This ensures that the final product satisfies the quality standards set and the objectives of the project initiation before bringing in the client.
The output document of the internal product testing activity is the Test Script.It lays out the details of the product testing carried out internally.
8. User Acceptance Test
The aim of this activity is to test the product’s acceptance by the users. The project sponsor carries out the user acceptance test to determine the acceptability of their final product by the users. The product could either be a success or a flop. This is why a user acceptance test is important. It gives the project sponsor a window to determine the next course of action.
They don’t have to heavily invest in a product that will only end up causing them a big loss but instead give them a chance to improve on the problems identified. The UATtest scriptis the output document for the user acceptance test activity. It therefore details the findings of the tests carried out on users in the user acceptance test activity.
Here, the project sponsor is tasked with deciding whether the test passed or failed. If the test indicates a pass, the process moves on to the last activity. If the test indicates a fail, another decision is run to determine if there is any change request required.
At this point, the project sponsor decides whether a change request is required on the product or not. If it is needed, the process moves to the implementation of the change request activity. It then rolls back to the internal product testing stage.
If not, the process moves on to the problem-solving stage. The underlying problem is solved, and then the process rolls back to the internal product testing stage.
9. Sign-off Deliverables Acceptance
This activity indicates the end of the quality management process. The purpose of this activity is to approve the deliverables of the project. The project sponsor accepts and approves the final products and deliverables of the project.
The output document of this activity is the Acceptance Document. It acts a proof of the project sponsor’s approval and satisfaction by the project’s deliverables and final results.
Conclusion
Quality management is not an independent and separate process that occurs at the end of the project lifecycle. Rather, it is a continuous process that should begin and end with the project. Thus, these activities must be implemented effectively to ensure the expected product quality is realized.

