The project monitoring and control process aims at tracking and reviewing the project and is undertaken from the initiation of the project to its closure. Various activities performed during this process assess if the project is being run in accordance with the established plan. This process is based on the PMBOK framework. This means it is a proven practice that is applied widely in project management.
Monitoring and controlling a project facilitate identification of deviations that pose a threat to successful completion of the project. If deviations are not identified and addressed, they result in unplanned and undesired project outcomes. Thus, this process ensures that abnormalities are detected and acted upon early on to prevent their escalation, which may lead to major and costly issues.
When unplanned issues are eliminated, there is an assurance that the project will be completed on time and that envisioned results will be achieved. There are several methods that are applied by project managers together with other key stakeholders to evaluate the project performance. Monitoring and evaluation consist one of these approaches and it should be undertaken regularly at different project phases. Doing that will make sure that issues that arise are recognized and addressed on time.
The objective of project monitoring and control process is to:
- Maintain accurate and up-to-date information about the project status and performance throughout the project lifecycle.
- Evaluate the actual performance of a project versus the desire and planned performance.
- Offer project estimations and performance insights that can be used to update the schedule and budget.
- Determine if corrective or preventive measures are required.
- Assess the effectiveness of effected changes and provide information that supports forecasting at different phases.
Concerning the scope of this process, monitoring and control is applied to but not limited to managing and controlling project works and risks, quality control measures, project performance in the entire lifecycle, controlling scheduling, and management of control of change throughout the project’s lifecycle.
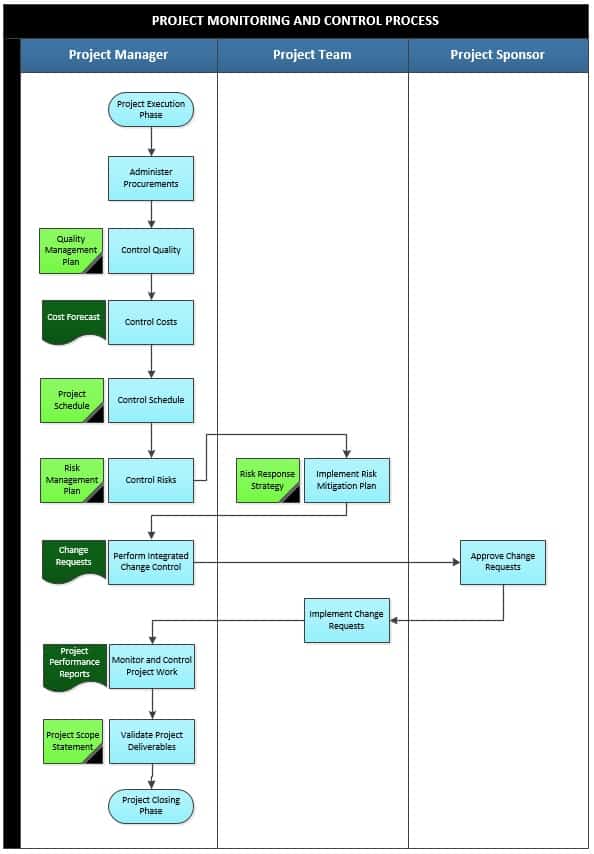
The following activities are performed during project monitoring and control phase:
1. Administer Procurements
This activity ensures to monitor the vendor to make sure that their performance satisfied the requirements of the contract. Moreover, this activity is used to make the required corrections and changes and to manage procurement relationships.
The project manager evaluates the sales deliverables using procurement performance measurement. Administering of procurements is accomplished through different techniques including contract change control system. Besides, the project manager refers to the contract, procurement documents, and performance information during the administer procurements activity.
2. Control Quality
The aim of this activity is to assess and make a determination on whether the activities are meeting the quality standards that have been established. In doing so, the project manager makes sure that various project operations and processes are implemented within the scope of project planning.
To accomplish this activity, the project manager relies on the quality management plan to identify the standards that have been established. These quality standards should be conformed as well as achieved to ensure project success. The project manager needs to be keen to understanding customer expectations and making sure that they are satisfied by the end product. The project manager refers to the Quality Management Plan to complete this activity successfully.
3. Control Costs
This activity is concerned with the supervision and management of project expenses. At this phase, the project manager needs to prepare for financial risks that might occur. During this activity, the expenses that are needed at various payment stages are identified and controlled. Besides, the project manager makes sure to manage the project budget. This is vital in order to ensure the appropriate use of finances and prevent shortfalls. Besides, spending money on unplanned events is controlled to prevent using money that is allocated to other uses. A Cost Forecast document is prepared during this activity.
4. Control Schedule
This activity seeks to monitor the status of different activities involved in a project. The activity also concerns making necessary updates to the project process and managing changes made to the schedule. By making comparisons between the scheduled baseline and project progress, a project manager determines whether certain project activities are behind or ahead of the schedule. Following this, correction actions are planned to ensure effective management of changes to the planned schedule. This activity eliminates the risk of late delivery of a project.
The guiding principle in this activity is that changes ought not to just be reacted but they should also be controlled proactively. Therefore, the project manager should act promptly to prevent changes from influencing or affecting the whole project schedule.
This includes preventing late project delivery by planning appropriate corrective actions for activities that are behind schedule. Besides, pending work plans should be reprioritized and relevant stakeholders should also be informed about the execution of planned work. During this activity, the project manager refers to the Project Schedule.
5. Control Risks
In all projects, risks are always present a project manager should have the ability to mitigate those risks proactively and envision potential risks as well. Effective methods for controlling risks required in project management. Control risks activity concerns implementing risk response plans. It involves monitoring residual risks, identifying new risks, tracking identified risks, and assessing the effectiveness of risk mitigation processes used during the project.
The risk manager goes through the risk management plan to familiarize himself with the identified risks. This helps to come up with appropriate and effective risk response strategies. A key advantage of the control risk activity is that it enhances stakeholders’ efficiency to manage risks during the project lifecycle. Besides, this activity motivates stakeholders to elevate their risk responses. The Risk Management Plan is consulted in this activity.
Related Articles:
- Project Initiation Process: 6 Key Activities
- Project Planning Process: 7 Key Activities
- Project Execution Process: 8 Key Activities
- Project Closing Process: 8 Key Activities
- Project Handover Process: 11 Key Activities
- Risk Management Process: 11 Key Activities
- Quality Management Process: 9 Key Activities
- Change Control Process: 8 Key Activities
- Issue Management Process: 9 Key Activities
6. Implement Risk Mitigation Plan
This activity aims to actualize the measure outlined in the risk management plan. This includes exploring available opportunities, restructuring the workforce, using the latest technology, and developing risk barriers. During this activity, the project team assesses the likelihood of unexpected happenings that can harm a project.
This is followed by identifying the most appropriate method for avoiding those events. Moreover, the project team goes ahead to implement planned actions that are aimed at reducing the effects of threats that are unavoidable. Collaboration with relevant agencies and companies is also initiated to share responsibilities regarding extremely risky activities. The Risk Response Strategy is referenced to undertake this activity effectively.
7. Perform Integrated Change Control
This activity focuses on measuring change impact on project limitations. Changes relating to different parts of a project can be requested particularly during the execution as well as monitoring and control phases. There is no need to implement all requested changes. Thus, this activity is performed to accept or reject changes based on an effective evaluation of their impacts.
All change or modification requests to baselines, deliverables, project documents, or project management plan are reviewed and either accepted or rejected based on their impact on the project. A key benefit of performing integrated change control is that it permits the consideration of documented changes in an integrated approach while minimizing project risks.
These risks usually arise from changes that are implemented without careful consideration of their impact on the entire project. A Change Requests document is prepared in this activity. This document is forwarded to the project sponsor for review and approval.
8. Implement Change Requests
This activity aims to incorporate into the project scope the change requests that have been approved. A project may fail to deliver the desired outcome if approved changes are not integrated into the project scope. The project team performs tasks and activities that will actualize the approved changes. Feedback on changes that have been done is provided. This is followed by an assessment of whether implemented changes were sufficient.
9. Monitor and Control Project Work
The aim of this activity is to track and review as well as report the project progress. This activity enables stakeholders to comprehend the project’s current status, schedule, budget, steps taken, and scope forecasts. Here, the project manager looks for any deviations from project plans. Identified deviations are assessed and relevant corrective actions are executed to avoid unplanned outcomes. The output document in this activity is the Project performance Reports.
10. Validate Project Deliverables
This activity concerns checking project deliverables to ascertain their correctness and completeness. The activity helps to know whether they meet the set quality criteria. Thus, the project manager makes an assessment of the outcomes against the results projected in the plans. Besides, all deliverables are reviewed to ensure they are satisfactory. The Project Scope Statement is referenced during this activity.
Conclusion
Project monitoring and control process helps to tract and review all metrics and tasks required to make sure that the authorized and approved project is on time, within budget, and on budget. Besides, the process ensures that the project work is carried out with minimal risks. Therefore, it is vital to master these activities and follow them accordingly to guarantee the achievement of the expected outcomes.

