The issue management process aims at managing issues that can be a threat to the achievement of the objectives of the project. This process helps in dealing with issues quickly and efficiently in order to keep the project on track. It runs throughout the project lifecycle, that is, from the initiation to closure stage.
Issues are present conditions or situations that are likely to cause an impact on the objectives of the project. They can therefore be termed as risks that have a 100% likelihood of occurrence. This makes it certain that even if they are not currently happening, they will surely happen sooner or later.
The issue management process helps in visualizing and tracking the personnel responsible for the issue resolution and how they are going to address each issues encountered.
Issue management process should be defined before the commencement of the project.. Risk identification helps the project team to deal with the predictable problems that may come up, and solve them before they occur and become issues. It’s therefore important to have a risk management plan before establishing an issue management process so as to ensure that all possible problems are solved before they actually burst out.
The objectives of the issue management process are:
- To clearly identify and record the issues.
- To properly document the issues
- To determine the impact of each issue.
- To prioritize issues and report on their status.
- To review all the issues and determine the next course of action.
- To take the necessary step and quickly resolve the issues.
The scope of the issue management process involves:
- Issue identification and documentation
- Analysis of the root cause of issues
- Designing issue action plan and implementing resolutions
- Reporting about project issues
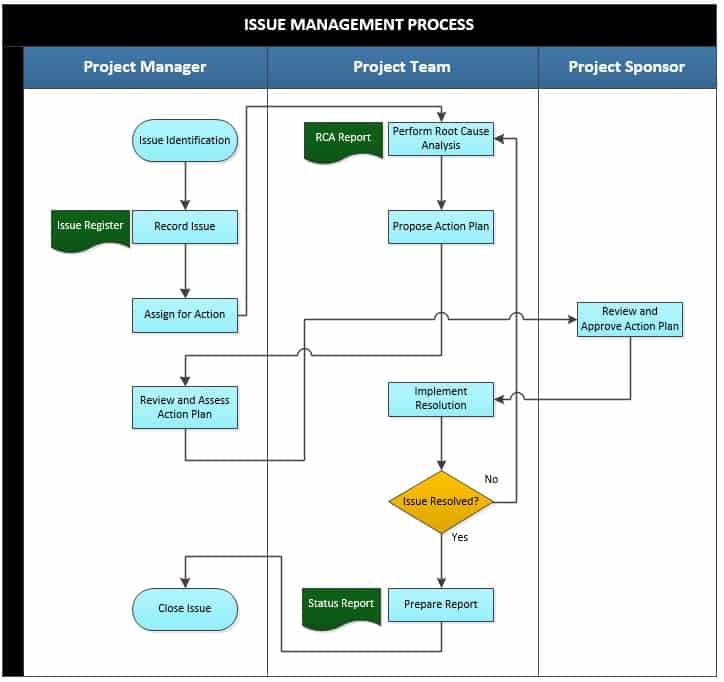
1. Issue Identification
The problems, gaps, inconsistencies, and conflicts that may be facing the project are acknowledged. The project manager identifies all the issues present or bound to occur in the project’s lifecycle. He also gathers all necessary information that may point out the possible issues.
2. Record Issue
The purpose of this activity is to record the issues as they happen. The project manager records the issues in order to provide a report and have a clear communication on the happenings of the project. It also makes it easier to track, investigate, and resolve the issues quickly and efficiently.
The record of the issue bears the type of issue, the identifier, the timing of the issue resolution, the description of the issue, and the manner of its priority. It should also bear who the resolution of the issue has been assigned to, the projected target date for the issue resolution, the status of the issue, the description of the action required for the issue resolution, and the final resolution of the issue. The issue register is the output document for the record issue activity.
3. Assign for Action
The aim of this activity is to assign people to different problems for them to tackle and track their progress. The project manager assigns the necessary personnel of the project team to take action on the issues identified. He also determines the action to be taken while assigning the responsibility and also sets a deadline for the resolution. Each issue is assigned to the person best equipped to tackle it.
The actions necessary for the issue resolution are assigned based on their priority levels, with the project’s most threatening issues being prioritized. This is because the issues that are of a higher priority may potentially derail the completion of the project, or even bring it to a complete standstill.
Issues that are of medium priority may also significantly affect the success of the project, but not to stall it completely, while issues of a low priority don’t necessarily affect the core objectives of the project or the crucial processes, but could end up creating a bigger problem if they are ignored for a long time.
4. Perform Root Cause Analysis
The objective of this activity is to carry out an analysis to find out what the root cause of the issues identified is. The project team performs the analysis to dig on the main possible causes of the issues raised. The root cause of the issues may cause the issues to recur from time to time.
Performing analysis for the root cause of issues is very crucial. This is because some issues keep on cropping up from time to time, and could only be solved through the resolution of their root cause. Otherwise, it would be much like treating the symptoms while the disease is still bottled up inside.
This is why the root cause analysis important, as it provides a full solution for the underlying issues, and gives an implication of the issue as to why it matters, and how much it matters. The output document for the perform root cause analysis activity is the RCA report.
5. Propose Action Plan
The purpose of this activity is to propose a detailed plan for problem-solving. The project team performs detailed planning for all the subsequent actions necessary to resolve the issues facing the project. It lays out all possible options for dealing with the issues at hand, along with an assessment for each action.
The project team is tasked with brainstorming on an action plan to be applied in resolving issues that are raised in the project. The action plan is drawn from the finding of the analysis performed on the project, and the identification of the root cause for the issues raised.
6. Review and Assess Action plan
This activity aims to review and perform an assessment on the proposed action plan to determine its viability in the resolution of the issues at hand. This helps in ensuring that the proposed action plan provides a solid solution to all the issues identified in the project.
The project manager reviews the proposed action plan to make sure that it incorporates a solution that is viable for the raised project issues. They also evaluate the action plan to ensure it fully resolves the issues at hand.
After a successful review and assessment of the action plan by the project manager, he recommends the action plan to the project sponsor for review and approval.
Related Articles:
- Project Initiation Process: 6 Key Activities
- Project Planning Process: 7 Key Activities
- Project Execution Process: 8 Key Activities
- Project Monitoring and Control Process: 10 Key Activities
- Project Closing Process: 8 Key Activities
- Project Handover Process: 11 Key Activities
- Risk Management Process: 11 Key Activities
- Quality Management Process: 9 Key Activities
- Change Control Process: 8 Key Activities
7. Implement Resolution
This activity aims at implementing the resolutions proposed for the issues at hand. This is the point at which the change happens. The project team creates a change request and handles the subsequent change control process.
The team also manages the consequential changes in the budget, schedule, or business case. This is because the issues being resolved may have caused an impact on the organization of the process, thus the need for adjustment on the budget, timeline, or the business case.
The implantation of the issue resolution should be prioritized. This is because some issues may cause massive losses if they remain unresolved for long or even end up needing escalation. The resolution implementation should also be monitored to make sure that the project remains on track.
After the completion of the resolution implementation, the project team is tasked with determining whether the issues raised were satisfactorily resolved. If the issues are found not to have been fully resolved, the process rolls back to the perform root cause analysis stage. This in turn results in an amendment on the RCA Report. If the issues are fully resolved, the issue management process moves on to the next stage.
8. Prepare Report
The purpose of this activity is to ensure that the status of the project has been properly documented and that all the key stakeholders are up to date in matters regarding the resolution of the issues of the project. The project team assigned to handle the issue prepares the report to ensure a smooth flow of information regarding the project to all key players.
Preparation of the status report ensures transparency and accountability during the process of issue management. This is therefore important as every action taken will be well accounted for, and the resources allocated will be properly utilized. The whole process will therefore be transparent and have minimal misuse of the resources utilized.
Report preparation is also an important aspect of good governance. A detailed report should be prepared for the issue management process. This also helps in detailing the issues for a better and precise understanding of the issues. The output document for the prepare report stage is the Status Report.
9. Close issue
The close issue activity marks the end of the issue management process.
Conclusion
Successful resolution of all issues in the course of the project lifecycle guarantees that achievement of the expected outcome. To effectively identify and manage issues, the steps in the issue management process should be adhered to.
Meta description: Following the activities in the issue management process ensures systematic management of all issues that may threaten project success.

