The purpose of the project initiation process is to initiate a project. Important questions on the necessity and achievability of the project are raised, and decisions made on the way forward. The project initiation phase is the stage whereby the goals, objectives and schedule of the project are defined. This process is based on the PMBOK framework. It is a proven practice that is applied widely in project management.
Key stakeholders of the project such as the project team and project sponsors are identified and brought together.
The project manager makes reference to the business case and the project proposal in order to understand the necessity of the project. Information needed is also gathered to evaluate time and cost estimates of the project.
The process initiation process constitutes activities that are aimed at defining the project. This process is finalized through the creation of the project carter, which outlines the purpose and requirements of the project.
The objectives of the project initiation process are:
- To define the purpose and the expectations of the project.
- To define the project scope to ensure that the project covers all the required aspects and full addresses them.
- To define clear milestones and timeline for the project to ensure a smooth flow of events throughout the project.
- To devise the project’s deliverables that are in line with the goals and the clients expectations.
- To identify all the stakeholders that are to be directly or indirectly affected by the project.
- To come up with an enough budget – at this stage, a budget estimation is made for running the project.
- To establish the risks, issues and interdependencies connected to the project – this would help the team prepare and plan beforehand to avert the risks and tackle the issues.
The key stakeholders of the project such as the project manager, project sponsor and the PMO use the scope of the project initiation process as the reference throughout the project.
The scope of this process covers:
- Project objectives
- Project Scope
- Deliverables
- Constraints
- Assumptions
- Exclusions
- Schedule
- Budget
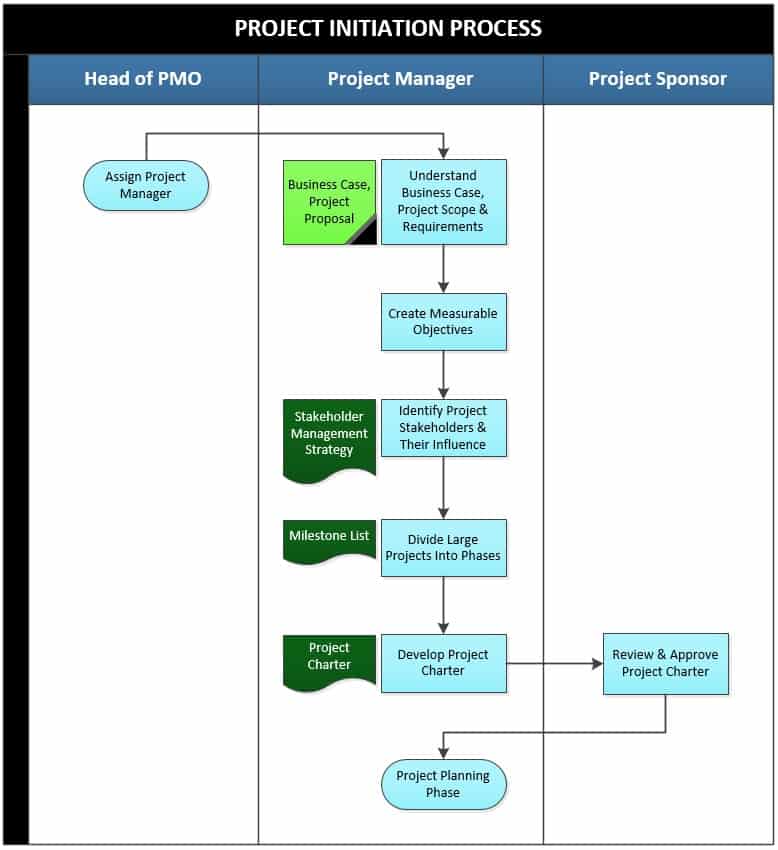
The project initiation process consists of the following activities:
1. Assignment of a Project to Project Manager
This is done in the process initiation process to authorize the involvement of the project manager from the beginning to the end of the project. This ensures that the project manager has an in-depth understanding of the project and can therefore identify imminent risks and constraints in the project. At this stage, the project sponsor as well as the client confirm their support for the project and releases the financial support required to begin working on the project.
2. Understand Business Case, Project Scope and Requirements
The aim of this activity is to comprehend the reasoning behind project initiation. Understanding the business case will allow stakeholders to know the justification for carrying out a project. Besides, going through the scope and requirement of the project helps to know the range within which the project will be undertaken the needs that should be fulfilled. The project scope will therefore act as the guide on what to be done, when and at what stage.
A good understanding of the project requirements will also help in the execution of the project in order to realize satisfaction for the organization. The project manager refers to the business case and identifies the elements of the project. The project manager should therefore consider the benefits, costs and risks rising from the project, and also the business context which covers the drivers of the business, the choices made and the options considered.
The project manager also refers to the project scope while developing a business case in order to maintain the context of the project. The project manager also refers to the project requirements in order to align the business case with the business needs to be addressed by the project. The project manager references the Business Case and Project proposal documents to conduct this activity effectively.
3. Create Measurable Objectives
This activity aims at establishing project goals to be achieved by the project. The project manager comes up with targets that can be measured at some point during the project lifecycle or after project completion. The project manager will aim at attaining those objectives to guarantee project success.
Coming up with measurable objective is important to avoid setting goals that cannot be realized given the available resources. Besides, these objectives guide the planning process and activities that will help to make the project a success. Thus, the project manager should make sure to create objectives that adhere to the SMART criteria so as to ensure that they are clear and concise, and most importantly achievable.
Measurable objectives are critical in assessing the performance of a project. This is because they are utilized by stakeholders to guide decisions regarding the management of different resources.
Related Articles:
- Project Planning Process: 7 Key Activities
- Project Execution Process: 8 Key Activities
- Project Monitoring and Control Process: 10 Key Activities
- Project Closing Process: 8 Key Activities
- Project Handover Process: 11 Key Activities
- Risk Management Process: 11 Key Activities
- Quality Management Process: 9 Key Activities
- Change Control Process: 8 Key Activities
- Issue Management Process: 9 Key Activities
4. Identify Project Stakeholders & Their Influence
The purpose of this activity is to establish the stakeholders, both internal and external, that will be affected by the project implementation, either directly or indirectly. This also involves establishing their impact on the project.
The project manager also needs to create strong relationships with the project stakeholders. The project manager therefore needs to analyze the stakeholders by assessing their interests, characteristics and motivations in order to determine their roles and levels of involvement in the project. The project manager also needs to measure the level on influence the stakeholders have to the project, and also what they want in return.
The more influence a stakeholder has on the project, the more support will be needed from them. The project manager should also keep stakeholders involved in the project through a proper and effective communication. This guarantees transparency throughout the project. The project manager should develop a management strategy for the stakeholders to establish ways to tackle negative impacts on the project, and instead increase the support. The Stakeholder Management Strategy is the output document for the Identify Project Stakeholders & their Influence activity.
5. Divide Large Projects into Phases
The purpose of this activity is to subdivide the project into phases to ensure a timely completion of the project. The project manager needs to identify the various tasks of the project on the basis of their time of completion, importance and their execution criteria.
The PM also needs to identify tasks that depend on the completion of other tasks. Milestones are also established with a clear timeline to ensure that all activities are completed in time and make sure that the project in completed within the stipulated time.A Milestone List is created at the end of the Divide Large Projects into Phases activity.
6. Develop Project Charter
This activity involves authorization of the project through documentation of project elements such as the objectives, constraints, stakeholders, risks identified and budgets involved in the project implementation. It therefore provides a foundation for defining the decisions of a project, and to ensure they are in line with the goals of the company.
The project charter therefore seeks to make the authorizations of the project formal. Its typical length is between one to two pages, but it may be longer depending on the size, type, and complexity of the project. The project manager therefore needs to establish the contents of the project charter. These may include:
- The goals or deliverables
- The scope
- Impact of the project on other business units and systems
- The project’s key stakeholders
- Milestones
- The budget estimation of the project
- The constraints, assumptions, dependencies and risks
- The success measurements of the project and the ROI
- Project approval
The development of the project charter marks the climax of the process initiation phase as it details the most crucial information about the project. It contains the purpose of the project, the most important project requirements, the major risks involved, the appointed project manager, a list of the main stakeholders, and the measureable objectives of the project.
An assumption log is also developed to illustrate the operational and strategic assumptions made and also what is expected of the project and the risks and issues likely to come up throughout the project. A project charter is therefore the output document for the Develop Project Charter activity.
After the successful development of the project charter, the project manager forwards it to the project sponsor for review and approval. The project sponsor evaluates the project charter to ensure it is in line with the project requirements. After ascertaining the correctness and appropriateness of the charter, the project sponsor approves it by appending a signature on the document.
Conclusion
In order to have an effective project initiation process, you need to clearly understand these activities. This will ensure that every activity will be perfectly undertaken to promote efficiency of the project, and achieve better results and the intended goals and deliverables.

