A business means performing many vital tasks and functions regularly. In a corporation, products are manufactured, the packaging is done, marketing activities are conducted, bills are paid, customers are served, and customer inquiries need to be answered. Whether a small or a big enterprise, you need people to perform all these jobs.
While starting a business, an entrepreneur has to wear many hats. Small business owners have to take on a lot of responsibilities. It is no wonder that many companies fail; there is so much to know and implement to be successful in business.
Like our human body, where different organs perform different functions, similarly, there are many functional areas within a business that various departments control.
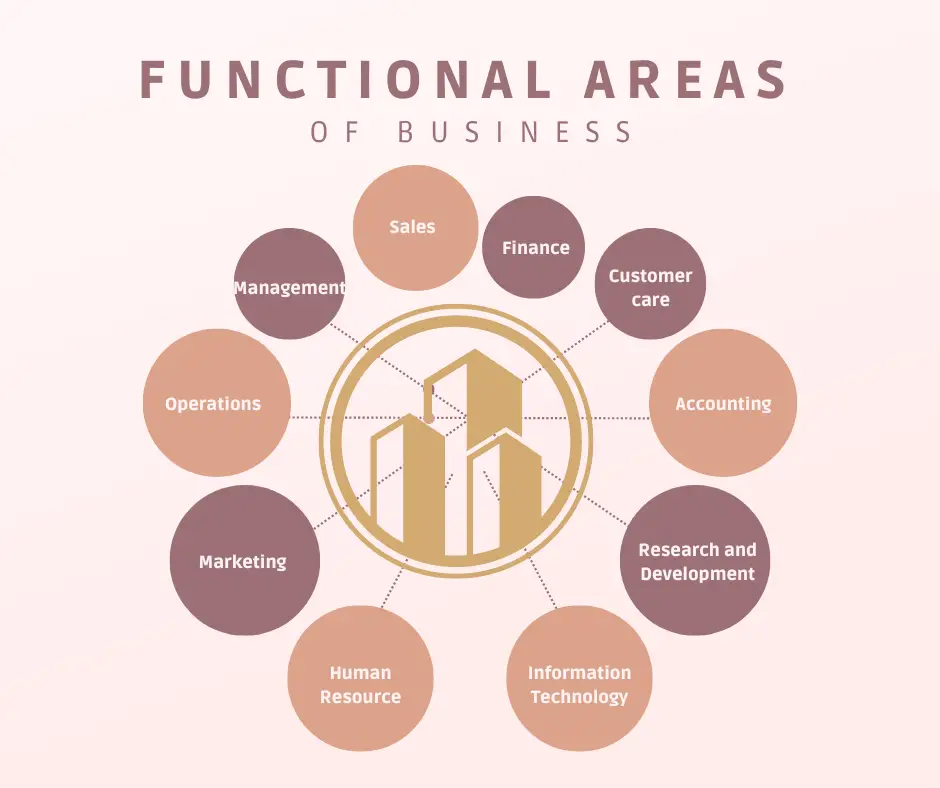
Functional areas can differ depending on the market’s nature and the business’s size. For instance, telecommunication providers emphasize technology optimization to provide premium services. In contrast, manufacturing companies look up to significant Research and Development (R&D) departments to stay in the lead in their respective business segments.
Retail companies may have no concern with R&D, but they heavily invested in Supply Chain Management.
A healthy business acts like a living organism with functional areas taking care of different divisions. These available domains collaborate skills and tasks to manage a company that has its protocols and logic.
Why Would A Company Organize By Functional Areas?
Business organization refers to an economic system where goods and services are exchanged against some value. A business organization is one where different processes are carried out to generate profits.
All business processes are conducted by functional areas, also known as ‘business units. Regardless of the business’s size, type or nature, each department is tasked with functions with a similar line of expertise or a defined focus.
If you own a small business, you will be doing many of the roles of these departments yourself —at least for the time being. But as your business expands, there will be too many tasks and responsibilities, so delegating tasks would be the safest and most practical option.
One of the key reasons to allocate business functions into different divisions is to allow them to operate within their area of expertise. This results in work efficiency and optimizes profitability across the business.
It is more efficient to have staff with similar skills group together. They can team up on projects requiring similar expertise.
The purpose of functional areas are
- Sales and marketing work in attaining goals linked to developing new markets or increasing sales.
- Human resources are tasked to arrange staff training activities and support the continuous professional development of all staff.
- Finance focuses on objectives and strategies linked to keeping costs low to improve profitability.
- Production sets targets relating to quality or meeting planned production schedules.
Functional Areas Of Business
The activities needed to operate a business can be divided into several functional areas: management, operations, marketing, accounting, and finance. Let’s briefly explore each of these areas.
| Business areas | Functional areas |
| finance | Cash management General ledger Payables/ receivables Inventory |
| Marketing | Research Customer segments Target market Demographics Media planning Brand strategy |
| Sales | Sales report Inventory reporting |
| Human Resource | Employees recruitment Retention Employee wellbeing Allowances |
| IT Administrator | System maintenance Setup App technology |
| Communication and customer service | Social media Email Video conferencing |
| Operations | Operational planning Strategy Quality control Forecasting Supply chain management |
1. Management
The crucial role of managers in a business surrounding is to supervise and manage business activities. They plan by setting goals and devise strategies around to achieve those goals. Most management activities take one of these roles.
| Planning: All commercial activities take the first route by planning short-term pathways to attain the company’s long-term goals. When goals are set, actions are devised accordingly.Organizing: The most functional part of a manager’s duties is efficiently organizing business operations using all the required resources. Controlling: A large part of the management goes into controlling each aspect of the business operations to ensure safety, profitability, and growth. Procedures, processes, and workforce all come under the light of management. Leading: Managers act as leaders for the organization in a practical way. The manager leads individuals, teams, or groups through new product development or introduction to new processes. When interacting with the community, customers, and suppliers, the manager becomes an organization’s leader. |
2. Operations
The operation functions in most organizations are not related to the equipment but include the business processes. From operational planning, forecasting, and supply chain management to ensuring customer satisfaction, many functions provide the best possible product or service to the customer.
Companies process their business by converting their resources(labor, material, information, and money) into usable form depending upon the type of business they are into. For example; Apple takes all its resources to produce tangible goods such as iPhone, Mac, watch, etc
Whereas hospital businesses work on resources to produce intangible goods in the form of services such as health care, nursing, hospitality, etc.
All the processes that involve turning resources into a usable, finished product are carried out by the operation manager.
The operations manager ensures the smooth flow of all these operations, monitors the entire process, and rectifies the errors at the initial stage. That will assist in improving the quality and productivity of the business operation and also help to enhance the organization’s profits.
| The functional areas of operations are strategy building, finance management, forecasting, quality control, and supply chain management. Converting raw resources into finished products either in the form of tangible products or intangible goods such as services. |
3. Sales
Sales generate business profit, so this department is the backbone of the whole structure. The functional sales area is to ensure sales goals and targets are achieved.
In a business setting, sales units play a significant role in bringing success to the organization. They oversee operations for generating revenue. The sales department is mandated to keep an eye on products and services and make sure they should result in profit.
The sales department gets in touch with the marketing teams and works on product launching, brand awareness, and rebranding. The sales responsibility starts right from the time the product comes from the product development. They develop ways how to sell the product to their target segment.
| Organizing sales promotionsAnalyze customer inquiries and take corrective measures initiated sales either in person, over the call, or through strategies preparing quotations for customers negotiating discounts or finalizing dealings for business customers providing technical advice keeping customer records up to date |
4. Marketing
For a business to run, you need customers, and to attract those customers, you need to invest in practical marketing activities.
The marketing department serves as the face of the company that helps to promote your product or services. It provides necessary insights into the target market and profitably anticipates customer needs and wants.
Marketers decide on the features and benefits of products including price and quality. They develop effective means of delivering the product to attract and retain customers.
They are vital for the company as they drive the business and help it achieve its organizational and financial goals. Their main line of duties include
| Outline marketing strategy organized market research to obtain feedback on new and existing products and services analyzing market research reports and advising senior managers about the results and imperatives used a variety of advertising and promotional platforms to market the product and service, e.g., press, campaigns, TV, social media, direct mail, Public Relations, trade shows, or exhibitions. Documenting a database of existing customers to target products and services appropriately. Designing and spreading public materials such as catalogs, flyers, or brochures assist with Designing, updating, and promoting the company’s offering |
5. Accounting
The most essential unit that assists the company in taking decisions regarding the allocation of company resources. This sector is important to represent the financial transaction that occurs between internal and external parties, investors, or government bodies.
They perform crucial functions such as
| Systematic tracking, recording, storing, and summarizing company financial transactions. Preparation of financial statements to help enterprises assess the financial strength of the organization. They provide information about budget, cost, asset allocation, and performance appraisalOversee monetary transactions and analyze financial information control fiscal policy, and form planning. |
6. Finance
Every Business functions in the realm of money. The company operates its finances, understands its cash flow, and strategizes the best use of monetary funds.
The functional area of your business related to finance include bookkeeping, or it can be a dedicated department keeping books and managing accounts. Either way, staying current on accounting tasks such as collecting or paying bills should be sufficient.
The finance department oversees the flow of money in the company. They deal with financial assets, draft account policies and take on debts.
They help the company to decide factors such as
- How much money a company will be needing?
- From where will the company gets the necessary funds?
- How and when will it pay the money back?
- What investments should be made in fixed assets such as plants and machinery?
- How much should be spent on research and development?
| Producing invoices, checking payments, and keeping a check on overdue paymentsRecord receivablesJournalize invoices receivedPayroll management producing statutory accounts each yearKeep a check on the accounts transactions. Issuing monthly budget reports to all departmental managers, including details about cash flow, forecasts, and periodic financial statements. Providing senior managers with information on sources of finance for capital expenditure. |
7. Human Resource
The Human resource department is a crucial component of the workplace. A study suggests that poor working HR will negatively affect the company’s productivity and performance. The time had passed when HR was confined to recruiting staff and maintaining paperwork.
Human resource takes a more strategic step to organize people in an organization. They assist the company in acquiring a competitive edge over its competitors.
The human resource department performs three significant roles; administration, people management, and change management. Besides recruiting staff and managing payroll, they work around employees to achieve their strategic goals by encouraging participation and maximizing employee performance.
Their line of work includes the following.
| market job vacancies form staff about promotion opportunities gather all job applications, arrange interviews, and publish candidates’ results inform new staff about their job roles and communicate information regarding the work environment conduct employees training sessions and engineering activities to foster professional growth supervised and monitor employees’ work performance keep a check on the well-being of the employeesJournaling sick leave and absence records carrying out Corporate social responsibility, e.g., long-service awards and company loansAdvise on the legal sides of the business and its employees liaising with staff associations or trade unions that represent the workforce |
8. Information Technology
In today’s era, no business can think of running without technology. It has become an integral and essential part of the organization that laid the foundation of a successful business. Despite managing computer-related tasks, it performs many vital functions, such as cyber security, business strategy, and system administration.
Nearly all businesses in the industry are reliant on IT services. Be it to serve customers, manage staff, or conduct research, IT provides valuable services to enterprises.
| Manages computer infrastructure of the company and contributes to revenue growth with improvements in organizational processes and procedures. Train employees on new systems. Contributes to the productivity and performance of the company provides electronic storage systems provides a remote working facility more tasks can be done in a short period of time |
9. Customer Service Department
The customer service department is the one that fulfills all customer needs. They serve as a representative in portraying your brand when interacting with potential buyers.
The customer service department is the decisive element of the organization that either retains or loses your potential customer. Excellent customer service means there are more chances that your customer is likely to return and make repeat orders.
| Delivering information about the company’s offerings answering customer inquiries and complaints about products and services providing after-sales service, for example, replacing damaged goods and getting them repaired dealing with customer complaints and troubleshooting them interpreting customer complaints to resolve problem areas collecting customer feedback to improve product service. |
10. Research And Development
The R&D department is responsible for keeping the business competitive by bringing innovative methods, designing new products, or updating existing ones. The R&D department primarily drives the business’s future growth.
The R&D department holds significant importance because it brings powerful insights about the market, leads to product improvements to optimize efficiency and reduce cost, and helps to thrive in competitive markets.
From the illustration below, you will know how the R&D department contributes to business success.
| The R&D department works around new medicines and drugs in the pharmaceutical industry. The R&D unit brings innovative tech methods to preserve food items such as ready meals, sauces, or flavorings in the food industry. Electronic and IT companies take R&D help to bring on new technology products and software, such as Smart Television, and PlayStation 5, and Engineers in the aerospace and car industries work on enhancing performance and safety while working to reduce emissions. Designers concentrate on the body and shape, both internally and externally. |
11. Distribution
The distribution department manages the entire supply chain of an organization. Effective product distribution increases customer satisfaction, reduces shipping costs, and handles delivery time to ensure corporate longevity, growth, and financial success.
The Distribution department carries out the following functions.
| They focus on the timely delivery of products ensuring all goods are safely stored before dispatch providing goods for dispatch are securely packed and correctly labels checking vehicle loads are safe and secure conforming products are delivered timelyMatch order delivery information and inform sales if there is a discrepancyFinalizing the delivery document planning, organizing, and scheduling vehicle routesInform sales staff about delivery schedules so that they can communicate with the customers troubleshooting distribution problems, e.g., through bad weather or vehicle breakdown. |
12. Production
The role of the production department is to convert raw materials into finished products. The unit controls the mass manufacturing of the product on a schedule. Whatever physical goods you see in the market are managed and manufactured by production. They work on product efficiency so that they can meet the output targets set by the company.
| Buying or ordering stocks of raw materials from approved suppliers storing and inspecting the supplies of raw materials scheduling production to maximize machine capacity and staff levelsManufacture and assembling finalized goods checking quality throughout the production process resolving delays issues Conduct routine machinery inspections and maintenance carry out repair work |
Conclusion
A business organization is a system designed to perform many commercial activities. To complete each role, the company has different departments. Just like a human body, the company is interconnected and dependent on each other.
Each of these departments offers various services and functions to facilitate the business processes, and none can operate without the others. The departments are staffed by different people with diverse backgrounds and skill sets. Depending on your area of competency, you can choose your role accordingly.

