An operations manager ensures that a business is performing at its best potential by overseeing multiple areas of operation. The operations manager’s primary responsibility is to ensure that business operations are running efficiently and that equipment and tools are working effectively. Operations manager are primarily concerned with planning, organizing, and supervising production, manufacturing, and provision of services. They design and control processes and also redesigns business operations in the production of goods or services.
An operations manager manages the entire production or service system. This process converts inputs (in the form of raw materials, consumers, energy, and labor) into outputs (in the form of goods and or services for consumers). Operations managers work in sectors like banks, hospitals, companies, suppliers, and customer service firms using technology.
Operation is a significant function in an organization and supply chains, marketing, finance, and human resources. Thus operation functions require management of both the strategic and day-to-day production of goods and services.
Several decisions are made in managing manufacturing or service operations, including product design, operations strategy, quality management, process design capacity, inventory control, production planning, and facility management. Each of these requires the capacity to analyze the current situation to improve manufacturing or service operations’ effectiveness and efficiency.
Operations Manager Job description
Operations managers interpret data from various departments, make strategic decisions, and roll out a plan of action. They can obtain their data from multiple departments’ reports, such as budgetary information, interpreting financial data, monitoring expense reports, and performing a cost-benefit analysis of internal programs. Operations managers’ report directly to the CEO or Board of Directors.
According to Robert, half the job description of an operations manager entails:
- Reviewing and interpreting operational data to assess the need for procedural revisions and enhancements. Participation in the design and implementation of specific systems to enhance revenue and operating efficiency
- Keeping up to date with carrier rule changes and distributing the information within the organization
- Providing, overseeing, and coordinating in the provision of training for new and existing billing staff on applicable operating policies, protocols, systems and procedure, standards, and techniques
- Analyzing trends impacting charges, coding, collection, and accounts receivable. Revising policies and procedures
- Participating in the development and implementation of operating policies and procedures
- Auditing current procedures to monitor and improve the efficiency of billing and collection operations
- Following up on claims using various systems
- Maintaining contact with other departments to obtain and analyze additional information to documents and process billing.
- Overseeing the functions of the billing department. Encompassing business coding, charging entry, claiming submissions, payment posting, accounts receivable follow-up, and reimbursing management
- Ensuring that the billing operations’ activities are conducted consistently with overall department protocol. Complying with general department protocol, federal state, and payer regulations, guidelines, and requirements.
- Developing production plans that assure that targets and production requirements are met accordingly
- Providing a solid leadership model for the employees and encouraging them to meet their targets.
Operations managers oversee their organization’s production of goods and services. They oversee various departments, such as purchasing, warehousing, and manufacturing. They must make sure their company’s products meet or exceed client’s expectations. The operations manager ensures the company runs smoothly and effectively. They may be involved in establishing sales and profit goals depending on the size of their company. Operations manager ensures their company safely conducts business. They emphasize compliance with safety environmental rules and regulations. They improve operational management systems, processes, and best practices.
Operations Manager Skills
An operations manager performs several roles including to plan, organize, and optimize business processes within an organization. The planning involves the alignment of processes across various departments. They ensure activities stay within budget. The budget is followed through buying the most cost-effective materials, streamlining production processes, appointing the right staff, or investing in modern machinery and technology.
The operations manager handles a wide variety of business functions depending on the industry. For an organization to function efficiently, it requires an operations manager with the right skills to confidently handle all the tasks. They need to have a combination of technical and soft skills.
Operations manager skills include:
- Interpersonal skills
- Practical verbal and written communication skills
- Analytical and problem-solving skills
- Excellent leadership skills
- Exceptional organizational skills
- Awareness of external and internal customer needs
- Adaptability
- Data processing skills and data entry skills
- Planning skills
- Ability to motivate team members
- Ability to track and measure staff performance
- Ability to oversee budgeting, reporting, planning, and auditing
- Understanding of necessary legal and regulatory documents
The operations manager plays a crucial part in the management team. They oversee high-level HR duties, such as attracting talents, setting training standards and hiring procedures. They also analyze and improve organizational processes and work to improve quality, productivity, and efficiency. Operations managers thus need to be adaptable to any scenario and need skills to support them through. With the correct balance of technical and soft operations manager skills, they can fulfill the demanding expectations of their role, no matter the situation.
Operations Manager Career Requirements
Formal education and experience for the operations manager job description vary a lot, according to the nature of the job duties and the type of company that employs an operations manager. However, the following are usually the necessities of this kind of job.
Qualifications for an operations manager include:
- A bachelor’s degree in business administration, commerce, management, industrial technology, or industrial engineering
- Knowledge and experience in organizational effectiveness and operations management
- Knowledge of human resource’s principles and practices
- Knowledge of business management principles and practices
- Fantastic information technology skills
- Knowledge of project management principles and practices
- Excellent knowledge on the use of software and hardware tools related to the operations manager job.
Operations Manager Salaries
Operations managers are compensated well for the crucial role they play in meeting organizational objectives. As operations managers move through their careers, their skills develop with each project that they complete. As such, experienced managers are highly sought after and are often offered higher wages in return for their expertise.
The average salary for an operations manager is $66,125 per year.
The highest-paid operations managers are from Delaware with an average salary 30% higher than the national average wage. Connecticut State follows with the average wage 28% higher than the average national salary. It is followed by New Jersey with an average salary 26% greater than the national average wage. New York follows with the average salary 25% greater than the average national salary.
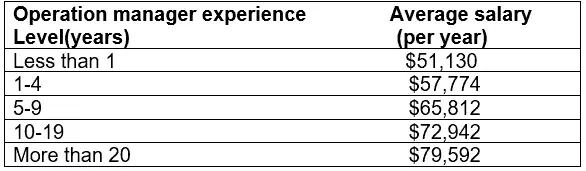
Operations manager pay, according to Payscale, is as follows.
Certifications Operations Manager
Operations manager certification is a professional achievement that is required in some cases as highly advantageous in others. It is useful for an operations manager who wants professional credentials. Certifications add value to the role of an operations manager. Some of the certifications offered by different organizations include;
- APICS – Certification in production and inventory management
- GSA – Operations and performance management professional certification
- AIBMC – certification in operations management
- GAQM – Associate in project management
A certification in operations management provides operations manager with a certain level of prestige and greater access to jobs with higher salaries. A certified operations manager has high performance and is successful in almost all their endeavors in an organization. Certification is seen as a sign of potential success and is valued by most employers. Operations manager certification is unbiased proof of operations manager talents and expertise. It is accepted worldwide and gives better career opportunities, credibility, and increased income for those who have acquired it.
As the business world continues to get more and more competitive, standing out from among competitors is crucial for success. Having operations managers on staff who are certified is becoming the norm in all types of industries. More and more government jurisdictions and some corporations require that their projects meet project management institute (PMI) compliance, which requires the operations manager to be certified.
The fundamental reason for an operations manager’s certification is that their projects meet quality standards and the stakeholder’s expectations.
Masters Degree for Operations Manager
Frequently, operations managers choose to pursue an advanced degree, such as a master’s in operations manager or any related field according to their passion. Having a master’s is important because, it helps demonstrate mastery of the concept involved in the area and gain additional experience to advance their careers. There are a lot of institutions that offer a master’s program in the operations management field. An operations manager can choose the institutions that best fit them.
Having a master’s in any operations management field helps operations managers to widen their knowledge and push into a business leadership role.
Operations Manager Tools and Software
Operations manager software makes sure that business operations, whether delivering services or products, are practical and efficient. Hence operations managers streamline organizations’ business processes as possible while providing the best possible results.
Software help businesses or organizations to obtain, track, monitor, and complete work orders. The software is a mixture of solutions such as; Ticketing software, which helps operations managers to create and manage customer requests. Work order management software allows operations managers to track the status of jobs and coordinate with service agents. Customer relationship management software helps operations managers to manage customer information and create marketing campaigns.
Some of the software used by operations managers include; business management software. This software controls business processes like product catalog, supply management, and project management.
The tools and software help ease business processes and communication between different teams in a company. They save time spent waiting for approvals, make documents readily accessible by keeping them on the cloud and allow the entire team to deliver impressive work.
The Role of Operations Manager in Project Management
Operations managers define the scope, budget, and schedule for operations projects. They manage the project team to execute operations projects effectively and efficiently. The managers develop the project budget in consideration of cost optimization and reduction goals. They ensure the project is completed within a defined budget and timelines. They manage resource assignments, work allocation, and lastly software and hardware requirements for operations projects.
Operations manager address questions and concerns of the project team, management, and customers professionally and confidently. They provide project status, delays, and issues to customers on time. The operations managers develop and implement project management procedures and methodologies to achieve business goals.
Nonetheless, operations managers conduct a project performance review and provide performance feedback to staff. They ensure the project deliverables meet customer expectations. Additionally, they identify project risks and recommend appropriate solutions operations. Operations manager track, monitor, and control expenses based on budgetary guidelines.
Operations managers generate new ideas in a project that will lead to the production of a new product. They ensure the product is excellent and meets the needs of a customer. They make predictions of events that will occur in the future based on past data. Operations managers rely on past and present data while formulating a project. They ensure there is excellent coordination from team members. They do so by dealing with interruptions, obstacles, crises and effectively going back to the normal routine functions to prevent further disruption.
Operations managers plan a project by mapping out exactly how to achieve a particular goal. They identify all the essential steps to accomplish the goal. They develop the necessary steps into a plan. Operations manager steps to achieve a goal may include increasing advertising, inventory, and sales staff. When the project is in place, the operations manager follows it to improve a company’s functionality. After setting a plan, the operations manager organizes their team and materials according to the list.
They then recruit, selects, and train the staff on how to handle the project. To achieve the project’s success, operations managers communicate effectively, guide, and motivate them to work smartly. Operations managers play a crucial role in project management. They are entirely in charge of ensuring a company project is successful. Thus they work proficiently and employ all the skills and experiences earned in various fields to ensure success.




