One of the most crucial tools when conducting a project is the project schedule. This tool conveys a wide range of details, including the deadlines, the tasks that need to be completed, the resources allocated to complete tasks, due dates, the milestones that are expected to be accomplished, and many more. Failure in keeping up with the schedule may lead to various negative impacts such as exceeding the budget aimed for the project, failure in quality checks for the deliverables, disappointment among stakeholders, and lastly it would disrupt the performance of the staff and stressing them out. In fact, nobody would be happy if the project falls behind the schedule regardless of which position they are in. Hence, in order to keep the schedule on track, project managers would employ a number of strategies such as PERT charts, Gantt maps, prioritisation matrix, and many more.
Another measurement that could be used to calculate how well a project is doing in relation to the initial schedule is known as the schedule performance index (SPI).
What is Schedule Performance Index
Schedule performance index (SPI) is one of the outputs under the earned value management (EVM). EVM is one of the widely known techniques used to evaluate the performance of a project by demonstrating how the completed progress corresponds to the benchmark set during the planning stage of the project. In simpler words, SPI could be defined as the schedule performance analysis of a project.
One of the other calculations that are often related to SPI is the schedule variance (SV). Schedule variance aims to calculate how much the actual work diverges from the expected schedule. The schedule performance index, on the other hand, measures the ratio of the work progress with the schedule. Regardless, both calculations are used to assess either the project is ahead, on, or behind the established schedule.
Schedule Performance Index in Project Management
It should be noted that the schedule performance index has its own disadvantages. There are several tips to be noted whenever you intend to use the schedule performance index for your project. Firstly, SPI does not provide the differences for critical or non-critical tasks. Some non-critical tasks that are progressing ahead of schedule may obstruct the critical tasks that are behind the schedule. Hence, it is crucial to be able to distinguish and prioritize the tasks according to the level of criticalness and complexity.
The other thing to consider is the accuracy of the data for the SPI. In order to achieve a reliable and accurate SPI, the data and reports for the process must be accurate too. If the SPI does not provide a precise value, it may display inaccuracy for the information of the project’s pace which may pressure the workers or worse, delay the completion of the project. The last thing to bear in mind is that in order to achieve a more accurate outline of the project’s performance, it is recommended to apply other project management techniques with the SPI values, not relying solely on SPI.
How to Calculate Schedule Performance Index
The formula of schedule performance index is:
Schedule Performance Index (SPI) = Earned Value (EV) / Planned Value (PV)
SPI = EV/PV
A further clarification of the formula will be elaborated in the latter part of this article.
There are several steps that ought to be followed in order when developing schedule performance index (SPI) which are:
Step 1: Calculating the percentage of completion for the project tasks.
Step 2: Determining the Planned Value (PV).
Step 3: Determining the Earned Value (EV).
Step 4: Determining the Schedule Performance Index (SPI).
Planned Value (PV)
Planned Value (PV), or its other name Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled (BCWS) refers to the number of tasks expected to be completed in accordance with the tasks budget. Its main emphasis is on the project’s budget.
For example, if a task is scheduled to be completed in a month and the budget expected is $10,000, by half of the month, the amount of budget used is approximately $5,000, which is also half of the total task budget. Below is the formula in calculating Planned Value:
PV = Percent Complete (planned) x Task Budget
Earned Value (EV)
On the other hand, Earned Value refers to the amount of tasks that are totally completed. It is also known as the Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP). This value is also determined from the budget of the project. The formula for Earned Value is as follow:
EV = Percentage of Completed Work x Budget at Completion (BAC)
The completed work comprises all the costs for the work including the transport, labour, equipment, licenses, and many more. The budget at completion is the total budget for the project.
For example, if the percentage of completion for a project is 50% and the budget is $5,000, the earned value is $2,500.
The corresponding Planned Value (PV) and the Earned Value (EV) must be determined individually for each task in order to measure the overall SPI of the project. Each project should firstly be segregated into more specific tasks and are assigned with the start and finish dates, and the budget for the task. This information would be the baseline in tracking the analysis of the schedule performance.
Schedule Performance Index Formula
The formula to calculate the schedule performance index of a project is as follows:
Schedule Performance Index (SPI) = Earned Value (EV) / Planned Value (PV)
SPI = EV/PV
From the calculation, these are the explanation if the SPI displays the following values. If the SPI is larger than 1, the project is ahead of the schedule. If the calculated value is smaller than 1, it indicates that the project is behind the schedule. Finally, if the SPI equals to 1, that means the project is on schedule.
Below is the indicator for the value calculated:
| SPI Value | Indication |
| 0 | The project has not yet started |
| 0.5 | Half of the progress expected achieved |
| 1.0 | The project is on schedule |
| 2.0 | The progress is twice as much as the expected schedule |
For an easy example, let’s say your project is targeted to finish in 4 weeks, and it is currently in the second week. The progress of your project should, by right, achieve completion of 50%.
Schedule Performance Index Examples
Let’s try to do an SPI calculation.
EXAMPLE 1
Project A is expected to be completed in 3 months and the budget allocation is $15,000. It is already in the mid of the second month and 50% of the project has been completed, signifying that the project is on schedule.

Earned Value:
EV = Percentage of Completed Work x Budget at Completion (BAC)
EV = 50% x $15,000
EV = $7,500
Planned Value:
PV = Percent Complete (planned) x Task Budget
PV = 50% x $15,000
PV = $7,500
Schedule Performance Index:
SPI = EV/PV
SPI = $7,500/$7500
SPI = 1.00
The value calculated for SPI is 1.0, indicating that the project is on schedule. Each hour of work spent for the job is worth every hour worth of work.
EXAMPLE 2
Project B is expected to be completed in 10 days and the budget allocation is $5,000. 6 days have passed and the percentage of work done is 75%.
It is already in the mid of the second month and 50% of the project has been completed, signifying that the project is on schedule.
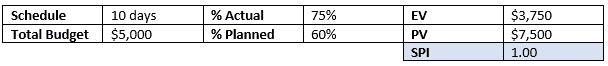
Earned Value:
EV = Percentage of Completed Work x Budget at Completion (BAC)
EV = 75% x $5,000
EV = $3,750
Planned Value:
PV = Percent Complete (planned) x Task Budget
PV = 60% x $5,000
PV = $3,000
Schedule Performance Index:
SPI = EV/PV
SPI = $3,750/$3,000
SPI = 1.25
The value calculated for SPI is 1.25 indicating that the project is ahead of the schedule.
Schedule Performance Index Calculator
Although the formulas are presented above, there are several online websites which feature SPI calculator to ease your tasks in calculating. One of the websites are AJDesigner.com (https://www.ajdesigner.com/phpearnedvalue/schedule_performance_index.php) and Project-Management.info (https://project-management.info/calculator-cost-schedule-performance-index-cpi-spi-variances/).
You may consider using the calculator to practice on calculating SPI in preparing for the PMP exam. Being certified with this Project Management Professional (PMP) may boost your career hence it is hoped that you could easily ace the questions on SPI to increase the chances of passing the exam with flying colours.
Schedule Performance Index (SPI) and Cost Performance Index (CPI)
In project management, SPI is used to measure the efficiency of the project schedule. The other metric known as the cost performance index (CPI), on the other hand, is used to measure the efficiency of the project’s cost. It calculates the ratio of cost spent to the amount of work completed.
The formula to calculate CPI is as follow:
Cost Performance Index (CPI) = Earned Value (EV) / Actual Cost (AC)
CPI = EV/AC
The value calculated for CPI provides indicators that are similar to SPI where CPI = 1 indicates that the project is on budget. CPI value of more than 1 implies that the amount of tasks completed exceeds the total amount of cost. Lastly, CPI lower than 1 indicates that the project is over budget.
To conclude, SPI is one of the commonly used techniques to ensure that the project progresses as expected from the schedule established. Although this technique is sometimes questioned due to its flaws, it could provide a rough idea of the performance of your project as expected from the scheduling. In order to fully utilize this technique, you may want to look into any project management software or tools that are equipped with the features relating to SPI.

